Integrating OpenAI ChatGPT with Spring Boot: A Comprehensive Guide
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to OpenAI ChatGPT and Spring Boot
Prerequisites
To successfully implement the OpenAI API with Spring Boot, ensure you have the following installed:
- JDK 1.8+
- Maven 3.X+
- Spring Boot 3.X+
- Lombok
- OpenAI API Key
Additionally, you will need the OpenAI API URL endpoint and model information. Below are the configurations to include in your Spring Boot application properties file:
# Please enter your own token to test this application
personal.openai.api.token=YOUR TOKEN
# OpenAI Properties
openAi.model=text-davinci-003
Configuring the API Key
The following code demonstrates how to configure the API key in your application. The API key is included as an authorization header parameter within the Spring Boot Configuration class.
@Configuration
public class ApplicationBeanConfigurations {
@Value("${personal.openai.api.token}")
private String personalOpenAiToken;
@Bean
@Qualifier("customRestTemplate")
public RestTemplate customRestTemplate() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.getInterceptors().add((request, body, execution) -> {
request.getHeaders().add("Authorization", "Bearer " + personalOpenAiToken);
return execution.execute(request, body);
});
return restTemplate;
}
}
Creating the Spring Boot REST Controller
Next, let's create a Spring Boot RestController to capture user input.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/v1/openAi/springBoot")
public class OpenAiWithSpringBootController {
@Autowired
OpenAiWithSpringBootService service;
@PostMapping
public List<String> submitOpenAiRequest(@RequestBody UserInput userInput) {
return service.submitOpenAiRequest(userInput.getUserCommand());}
}
@Data
public class UserInput {
String userCommand;}
Implementing the OpenAI Service
Now, we will create a Spring Boot Service class that will invoke the OpenAI API and handle the responses from ChatGPT.
@Service
public class OpenAiWithSpringBootService {
@Value("${openAi.model}")
private String openAiModel;
@Value("${openAi.url.endpoint}")
private String openAiEndpoint;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("customRestTemplate")
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private static final Double TEMPERATURE = 0.3;
private static final Double TOP_P = 1.0;
private static final Integer MAX_TOKENS = 60;
public List<String> submitOpenAiRequest(String inputCommand) {
OpenAiRequest aiRequest = OpenAiRequest.builder()
.maxTokens(MAX_TOKENS)
.temperature(TEMPERATURE)
.topP(TOP_P)
.model(openAiModel)
.prompt(inputCommand)
.build();
ResponseEntity<OpenAiResponse> restCallResponse =
this.restTemplate.postForEntity(openAiEndpoint, aiRequest, OpenAiResponse.class);
if (HttpStatus.OK.equals(restCallResponse.getStatusCode())) {
OpenAiResponse aiResponse = restCallResponse.getBody();
return aiResponse.getChoices()
.stream()
.map(choice -> choice.getText().replaceAll("[nr]", ""))
.toList();
} else {
return Collections.singletonList("An error occurred with the OpenAI API.");}
}
}
Understanding the OpenAI API Request and Response
We created a Data Transfer Object (DTO) class to align with the request and response structures of the OpenAI API.
@Data
@Builder
public class OpenAiRequest {
private String model;
private String prompt;
@JsonProperty("max_tokens")
private Integer maxTokens;
private Double temperature;
@JsonProperty("top_p")
private Double topP;
}
#### Key Parameters Explained
- Model: The machine learning algorithm employed to analyze data patterns. We will utilize text-davinci-003, which is particularly effective for language tasks.
- Prompt: This parameter allows users to interact with the model and receive relevant answers.
- Max Token: Represents the maximum number of tokens (pieces of words) the model will use to formulate a response.
- Temperature: Adjusts the randomness of the output; lower values yield predictable results, while higher values generate diverse outputs.
- Top P: An alternative method to control randomness; OpenAI recommends using either Temperature or Top P, not both.
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
@Data
public class OpenAiResponse {
private String id;
private String object;
private LocalDate created;
private String model;
private List<Choice> choices;
private Usage usage;
}
@Data
public class Choice {
private String text;
private Integer index;
@JsonProperty("finish_reason")
private String finishReason;
}
@Data
public class Usage {
@JsonProperty("prompt_tokens")
private Integer promptTokens;
@JsonProperty("completion_tokens")
private Integer completionTokens;
@JsonProperty("total_tokens")
private Integer totalTokens;
}
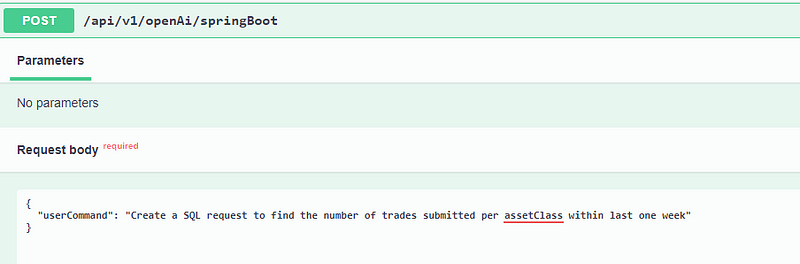
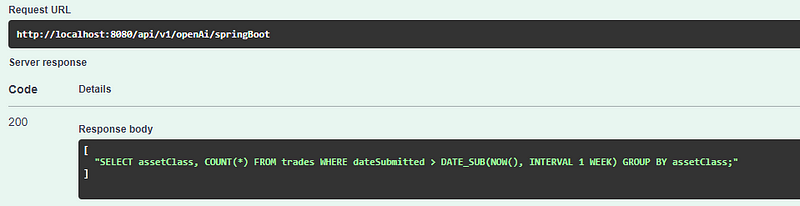
Example of API Interaction
Below is an illustration of how the integration functions. By inputting a SQL query in plain language, ChatGPT generates the corresponding SQL syntax.
OpenAI API Request JSON BODY
{
"model": "text-davinci-003",
"prompt": "Create a SQL request to find the number of users as per assetClass who have made more than 100 requests per day",
"temperature": 0.3,
"max_tokens": 60,
"top_p": 1,
"frequency_penalty": 0,
"presence_penalty": 0
}
OpenAI API Response JSON BODY
{
"id": "cmpl-7WpzLx4N5MHwfE9wrgEcuNltEoQoh",
"object": "text_completion",
"created": 1688060695,
"model": "text-davinci-003",
"choices": [
{
"text": "nnSELECT assetClass, COUNT(*) nFROM users nWHERE requests > 100 nGROUP BY assetClass;",
"index": 0,
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 23,
"completion_tokens": 28,
"total_tokens": 51
}
}
Chapter 2: Conclusion and Further Reading
This video titled "Spring Boot + OpenAI ChatGPT API Integration | JavaTechie" offers a detailed overview of the integration process.
The video "Integrate ChatGPT with Spring Boot: Step-by-Step" provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide to the integration.
Thank you for reading! If you found this helpful, consider checking out the GitHub code reference for this article. Don't forget to show your support with a clap and subscribe for more content. You can also follow me on LinkedIn, Twitter, and GitHub. For those interested in supporting my work, feel free to visit my BuyMeACoffee page.
