The Emergence of AI in Military Applications: A New Era
Written on
Chapter 1: The Intersection of AI and Military Strategy
The integration of artificial intelligence in military operations is not merely about developing advanced weaponry or accelerating decision-making during conflicts. Instead, it represents a complex interplay of authority, ethics, strategy, and technological advancement.

In an era marked by rapid technological advancement, AI stands out as a pivotal force, revolutionizing various sectors, including healthcare and finance. However, its most significant influence may be found in the military domain, where the implications are profound. This melding of military and AI extends beyond the battlefield; it indicates a fundamental shift in how nations strategize, defend, and position themselves globally. This article will examine the evolving relationship between the tech industry and military, often referred to as the Military-Tech Complex, and the specific applications of AI within the defense sector. Future discussions will delve into the roles of drones and robotics in warfare.
Section 1.1: Silicon Valley's Military Ties
Before assessing the current dynamics between technology and the military, it's essential to explore the historical context of Silicon Valley and the influence of defense funding in its inception. The popular narrative suggests that Silicon Valley emerged from engineers launching startups in garages, backed by visionary investors. However, this oversimplification overlooks the more complex truth.
Long before Apple and Google emerged, the tech companies in Silicon Valley predominantly catered to a singular client: the U.S. government. The region's innovation was primarily fueled by defense contracts aimed at enhancing America's technological edge globally.
The military-tech relationship dates back to pre-World War II, when innovations such as radio technology began to take root in the Bay Area. This was soon followed by advancements in radar and electronics during the war. In the 1940s and 1950s, U.S. governmental funding supported universities in their pursuit of technology improvements for weapon systems, driving innovation in radio, radar, transistors, integrated circuits, and computers. These government contracts provided crucial funding that propelled foundational research, creating a revenue stream alongside early commercial sales.
Fred Terman, a key figure in Stanford University's engineering program, played a significant role in fostering this ecosystem. He encouraged his students and faculty to translate their research into startups that catered to defense contractors. The myth of the college dropout entrepreneur taking their idea to market can trace its roots back to this period, emphasizing the military's influence on early tech development.
To better understand the historical context of Silicon Valley, I recommend watching a video from The Cynical Historian, which outlines its evolution. For a deeper dive into how military research and funding fueled the tech boom, consider Steve Blank’s lecture on the Secret History of Silicon Valley.
From the 1970s onward, venture capital began to play a more prominent role in the valley, shifting the focus towards profit-driven models aimed at commercial markets rather than government contracts.
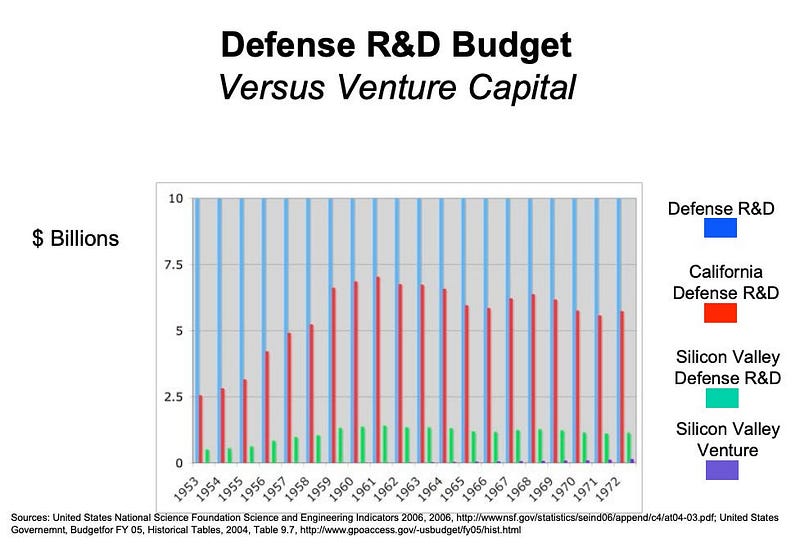
The rise of venture capital funding, centered on profitability, transformed Silicon Valley's landscape, leading to the emergence of companies like Apple and Microsoft. In contrast, defense projects aimed primarily at advancing military technology, allowing for greater freedom in exploration and innovation. Many technologies we now take for granted, such as the Internet and GPS, originated from military research initiatives.
The shift towards a VC-funded model created a hesitancy among new tech companies to engage with defense agencies. Many founders, influenced by counterculture movements of the 1960s and 70s, held pacifist views and harbored distrust towards authority, which shaped their companies' early ideologies.
However, many tech firms still benefited from government-funded research projects. The Internet, initially developed under ARPA (a Department of Defense entity), evolved into the global network we now know, fueling the growth of tech giants such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook.
As machine learning technologies advanced in the 2010s, capturing the military's attention, the Algorithmic Warfare Cross-Function Team (AWCFT) — commonly referred to as Project Maven — was established in 2017. This initiative aimed to leverage AI capabilities for military applications, fostering partnerships between the Department of Defense and various tech firms, including giants like Amazon and Microsoft as well as specialized startups.
Project Maven garnered significant attention due to controversy surrounding Google’s involvement. Initially, Google provided AI technology for processing drone imagery, enhancing human analysts' ability to identify potential targets. However, after employee protests and public criticism, Google withdrew from the project in 2018. This incident ignited discussions about human rights and the ethical ramifications of developing AI for military applications, prompting many AI researchers to pledge against working on lethal AI technologies.
In a similar vein, the Joint Enterprise Defense Infrastructure (JEDI) contract aimed at integrating cloud computing into military operations faced challenges. After Microsoft secured the $10 billion contract over Amazon, legal disputes arose, leading the Department of Defense to cancel the project.
In 2021, when Spotify's founder, Daniel Ek, invested in Helsing, a company focused on AI solutions for defense, many Spotify users expressed outrage at their subscriptions funding military technology.
Everything shifted with the onset of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, which triggered a global reevaluation of military spending.
The first video titled "The Impact of AI on Warfare, With Andrew Reddie" explores how AI technologies are reshaping modern military strategies. As nations reassess their military capabilities, increased investments in defense technology, particularly AI, have become paramount.
Section 1.2: The Arms Race and AI Investments
The events of February 2022 marked a turning point in global military spending, particularly in Europe, where many nations recognized their outdated defense systems and initiated extensive upgrades.
In the wake of the Ukraine conflict, several European countries, including Germany and Poland, announced significant increases in military budgets, much of which is designated for new equipment and emerging technologies, with a focus on AI.
On June 20, 2022, NATO launched the Innovation Fund to foster transformative technologies, pledging over €1 billion to early-stage startups working on dual-use technologies. This includes AI, big data processing, and automation among other innovations.
Parallelly, the European Defence Fund (EDF) committed to investing €1 billion into collaborative defense research, targeting future security challenges and aiming for an eventual €2 billion in investments by 2027.
The UK also introduced a Defence Artificial Intelligence Strategy, aspiring to be a leader in AI applications within military contexts, while Germany allocated a portion of its significant military investment towards AI research.
In the U.S., initiatives like the Defense Innovation Unit and AFWERX aim to stimulate growth in advanced military technologies, encouraging collaboration between big tech and startups.
The second video titled "Information in War - Military Innovation, Battle Networks, and the Future of Artificial Intelligence" discusses how military innovation is being reshaped by AI and information technologies.
Chapter 2: The Military-Tech Complex: A New Paradigm
Big tech companies are following the established path of earlier defense contractors, embedding themselves within governmental frameworks to secure their roles in national security, essentially becoming "too big to fail." This development mirrors the historical formation of the military-industrial complex.
One method of establishing this military-tech nexus is through direct collaboration with government entities, as seen in Project Maven and JEDI. Another route involves partnerships with established defense contractors, exemplified by Microsoft’s alliance with Leidos to deliver AI solutions for public sector applications.
Startups are also eyeing lucrative defense contracts, which, while more challenging to secure than civilian contracts, can lead to substantial long-term agreements. Government grants can similarly provide essential support for startups seeking to establish their market presence, akin to earlier tech ventures from the 1950s to the 1970s.
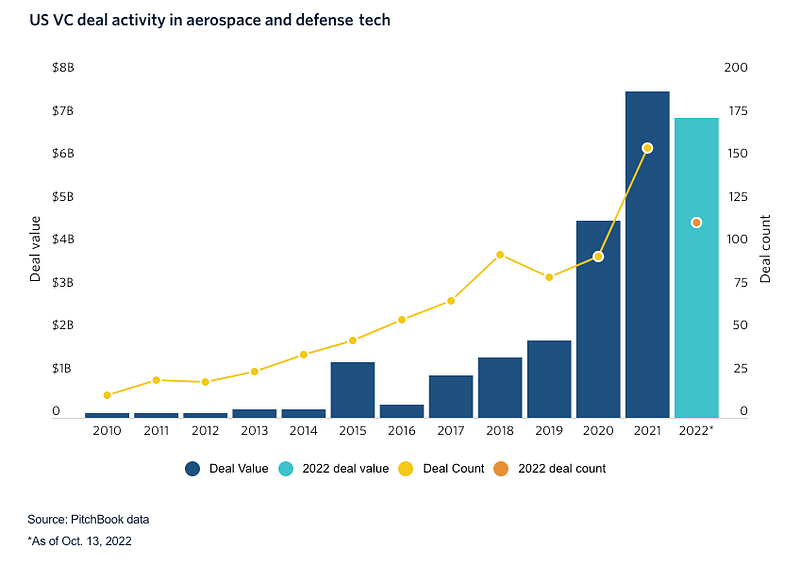
However, entering the defense sector presents unique obstacles. Many venture capital firms are hesitant to invest in startups focused solely on defense, often preferring dual-use technologies. Nevertheless, the landscape is evolving, with increasing openness towards defense-focused investments. In 2022, U.S. VC firms invested over $7 billion in the defense sector.
Seeing the potential in the expanding defense sector, Amazon launched the AWS Defence Accelerator in 2022 to support UK and European startups utilizing cloud technologies for military applications. Following its success, AWS initiated the 2023 European Defence Accelerator, expanding its cohort of supported startups.
Notable Players in the Military-Tech Space
Palantir is among the prominent entities in this arena. Founded in 2003, it initially concentrated on defense and intelligence sectors before branching into other industries. The company has faced scrutiny for its ties to government agencies, including the CIA and NSA.
Following the outbreak of the Ukraine conflict, Palantir offered its services to European nations and later claimed that its software significantly contributed to military operations in Ukraine.
Palantir recently introduced Palantir AIP, a large language model designed for military commanders, allowing operators to query information about enemy positions and facilitate decision-making in real-time.
Andruil, founded in 2017 by Palmer Luckey, is another notable player, recognized for its controversial stance on military partnerships. The company provides various autonomous systems and surveillance technologies, heavily utilizing machine learning.
Helsing, inspired by geopolitical events like Russia's annexation of Crimea, is creating a battlefield operating system that aggregates data from various sources to enhance situational awareness for military personnel.
Improbable, which began as a metaverse company, has transitioned into defense contracting, providing simulation technologies for military training.
Kodiak, while focusing on autonomous logistics, has gained attention from the military for its potential applications in reconnaissance and supply operations.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Military AI
The ethical implications of weaponizing AI are complex and contentious. A primary concern revolves around the autonomy of AI systems in making life-and-death decisions. As AI can effectively identify and track targets, questions arise regarding accountability and the potential for machines to initiate lethal actions without human oversight.
Reports indicate that some military drones may utilize AI for autonomous targeting, raising concerns about the erosion of human control in critical decisions. The accountability for potential war crimes committed by autonomous systems remains murky, posing challenges for legal and ethical frameworks.
The rapid advancement of AI technologies also raises fears of an arms race that could destabilize international relations, as nations invest in military AI capabilities, potentially lowering the threshold for conflict engagement.
Ultimately, the ongoing debate regarding the long-term risks posed by superintelligent AI systems emphasizes the necessity for careful regulation and oversight in AI research.
The Future of AI in Military Operations
The military's adoption of AI technologies is inevitable, as they offer significant advantages in situational awareness and operational efficiency. Historically, technological innovations have continuously reshaped military strategies and outcomes. Now, it is AI's turn to influence warfare profoundly.
The future of military AI will depend on how responsibly we harness its potential, shaping not only the outcome of conflicts but also the broader geopolitical landscape and the future of humanity itself.
If you found this article insightful, consider following for more content like this. Your support helps fuel further exploration into the intersection of technology and human experience.