Revolutionizing Computing: MIT's Breakthrough in Analog Synapses
Written on
Chapter 1: MIT's Analog Synapses
At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), an interdisciplinary team is pioneering the development of artificial analog synapses. Remarkably, they have achieved synapses that outshine biological synapses in the human brain by a staggering factor of one million.
The innovative synapses crafted by MIT utilize phosphosilicate glass, which significantly surpasses human synapses in terms of performance. Recently, the team unveiled an upgraded version of these synapses, which operates a million times faster than its predecessor. The foundation of these analog synapses is an inorganic substance known as phosphosilicate glass (PSG).
Through PSG, researchers are constructing programmable resistors that are analogous to the transistors found in modern processors. Their ambition is to establish the fundamental components for a specialized analog processor aimed at advancing deep learning within artificial intelligence.
Section 1.1: The Implications of Rapid Advancements
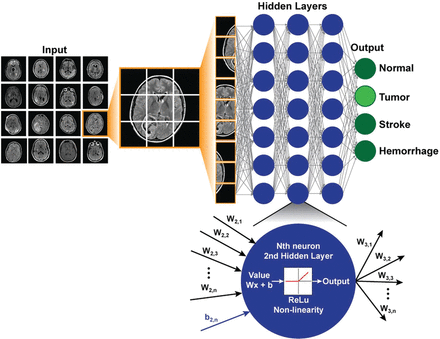
This topic is undeniably thrilling, holding immense potential. While some may view these advancements with trepidation, fearing a swift replacement of humanity by machines, the reality is likely more nuanced. Full realization of this technology may still be years away; however, the strides made in fields such as industry and medicine—particularly in deep learning that mimics human cognitive processes—are remarkable and increasingly mainstream.
Section 1.2: Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
What stands out is the enhanced computing efficiency coupled with a significant reduction in energy consumption. The growing concern over energy usage is pressing, especially considering the electricity demands of data centers, financial markets, and blockchain technologies. If successful, these innovations could offer sustainable solutions for our planet’s energy challenges. While the path ahead remains long, history has shown that groundbreaking technologies—like personal computers and the internet—may surprise us with their rapid adoption.
Chapter 2: Understanding the Learning Process
The first video titled "How Artificial Intelligence Learns Like The Human Brain | MIT Sloan and MIT CSAIL" explores the parallels between AI learning processes and human cognition, shedding light on the implications of MIT's advancements.
The second video, "How Do Neural Networks Grow Smarter? - with Robin Hiesinger," delves into the evolution of neural networks and their increasing intelligence, providing a deeper understanding of the technology driving these innovations.
Sources and Further Readings
[1] The Brussels News, MIT creates artificial neuron 1 million times faster than in human brain (2022)
[2] t3n, Analoges Deep Learning: MIT-Team entwickelt analoge Synapsen, die menschliches Gehirn übertreffen (2022)
[3] AJNR, Deep Learning in Neuroradiology (2018)