Transforming Conversations: The Impact of AI and LLMs
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding AI Conversations
Discover how Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Bard are revolutionizing human-machine interactions. These advanced technologies enable more fluid, engaging, and informative conversations than ever before.
Are you curious about the excitement surrounding LLMs, AI-driven dialogues, and Prompt Engineering? If you're eager to learn how these innovative tools can significantly enhance your everyday experiences, you’re in the right place! This article will take you through the captivating realm of AI conversations, revealing the magic behind LLMs.
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
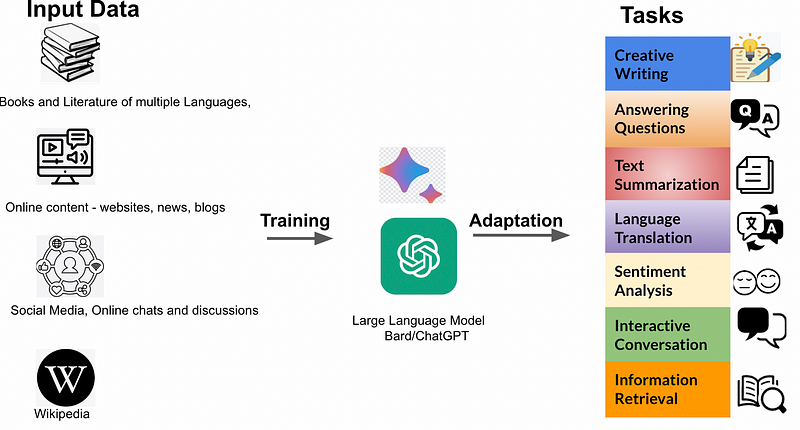
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an exceptionally advanced machine trained on an extensive array of text data, comprising sources such as books, articles, online content, and social media discussions. This extensive training endows LLMs with a profound understanding of the world.
Notable examples of LLMs include ChatGPT, Bard, and Perplexity. With an LLM at your fingertips, you can request various tasks, such as answering inquiries on countless subjects, summarizing lengthy texts, translating between languages, or analyzing the sentiment of a piece, which aids in grasping its emotional undertone.
Inspired by Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models
LLMs can be employed in numerous ways: inquire about climate change, seek a book summary, translate text, or ask for sentiment analysis on various documents. Have you ever pondered how LLMs like ChatGPT acquire their knowledge?
The "GPT" in ChatGPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformers. These models utilize a robust deep-learning framework known as Transformers, which harness artificial neural networks to learn from vast data sets.
LLMs learn by consuming a wide variety of text data, breaking it down into smaller components termed "tokens." These tokens can represent individual words or even smaller fragments within a sentence.

Understanding Sentence Tokenization
By grasping the connections between these tokens, LLMs can interpret context and long-range dependencies within sentences, resulting in coherent and informative text generation.

Transformers possess an exceptional capacity to learn from extensive language datasets, often training on far more information than any human could process in a lifetime. This extensive training equips them with a comprehensive understanding of language, applicable across diverse contexts.
In essence, Transformers absorb vast amounts of information, enhancing their language comprehension and text generation abilities. The core of Transformers is the Attention mechanism, which allows LLMs to effectively process language by prioritizing different segments of the input text during output generation.
Think of it like reading a book—you're not only focused on the words but also the meanings, tones, and overall structure. Similarly, the Attention mechanism allows Transformers to discern relationships among various input text components.
Learning through Reinforcement with Human Feedback
LLMs learn tasks through a combination of trial-and-error and guided instruction. This dual approach is embodied in Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF). In RLHF, the LLM is assigned a task and presented with examples. The model attempts to execute the task, receiving human feedback on its performance, which fine-tunes its internal understanding.
Human feedback enhances the learning process by enabling the LLM to learn from mistakes rather than starting from square one, making its outputs clearer and more comprehensible.
What Tasks Can LLMs Perform?
LLMs are a versatile form of artificial intelligence capable of tackling an array of tasks.
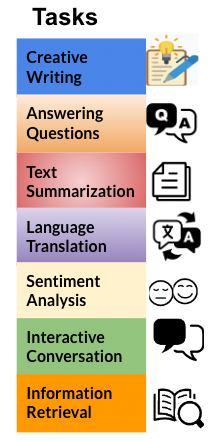
Creative Writing: LLMs can craft imaginative texts, including poems, code snippets, and essays.
Question Answering: LLMs understand and respond to inquiries contextually, enhancing customer service interactions.
Text Summarization: LLMs condense extensive text into concise summaries while retaining essential information.
Language Translation: LLMs facilitate communication across language barriers.
Sentiment Analysis: LLMs evaluate text to ascertain emotional tones, useful for analyzing customer feedback.
Interactive Conversations: LLMs foster engaging discussions, enhancing educational experiences and customer relations.
Information Retrieval: LLMs streamline information searches by generating relevant and personalized results.
Popular AI Conversation Tools
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT
- Google’s Bard
- Perplexity AI
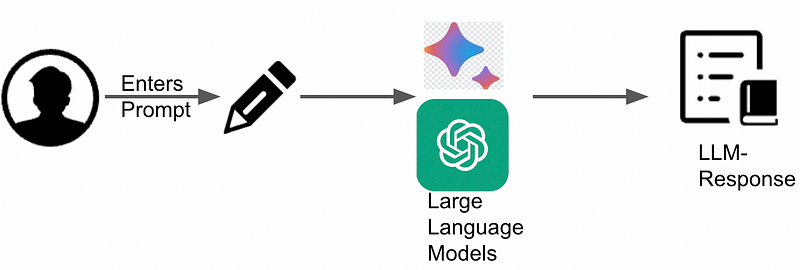
Understanding Prompts
A prompt is a directive for an LLM, guiding its actions. The prompt's clarity and specificity directly influence the quality of the generated output.
Examples of Effective Prompts
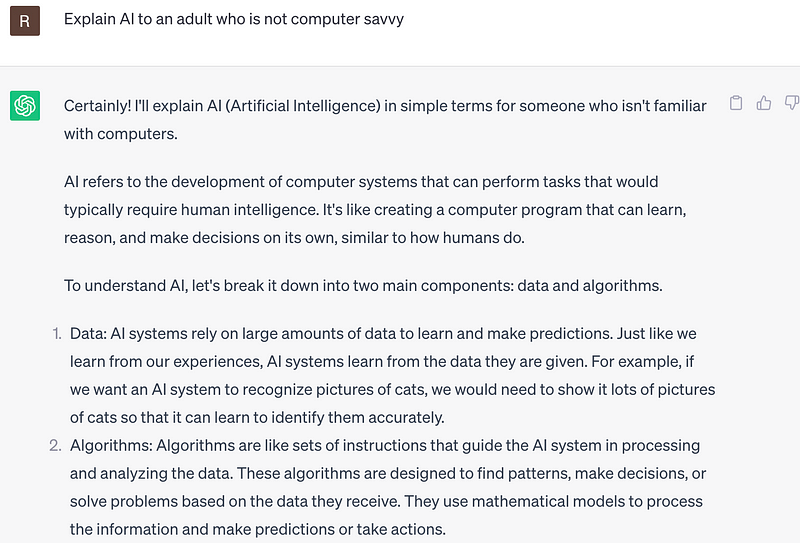
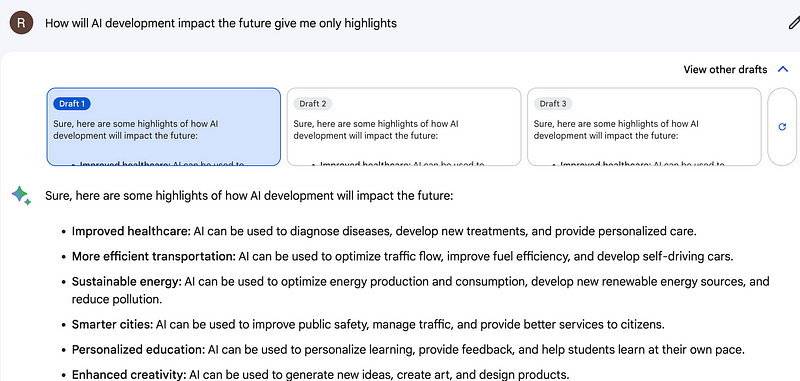
Remember, poorly structured prompts yield generic results. Mastering prompt construction is vital for unlocking the power of LLMs.
Building Blocks of a Prompt
A prompt consists of several components: Instruction or Task, Context, Example, Input Data, and Output Indicator. Depending on the application, not all components may be necessary.
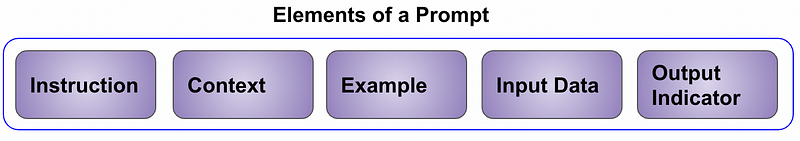
- Instruction: The directive specifying the task.
- Context: Background information relevant to the task.
- Example: A demonstration of the desired output.
- Input Data: The specific question or topic for which a response is sought.
- Output Indicator: The format or length of the expected response.
Best Practices for Writing Prompts
The quality of LLM responses hinges on the prompts provided. Here are some best practices:
- Clarity and Specificity: Provide clear, specific instructions to avoid ambiguity.
- Contextual Definition: Clearly articulate the context of the task.
- Chain of Thought (CoT): Encourage the LLM to articulate its reasoning step by step.
Features of a Good Prompt
A successful prompt should:
- Align with the user's intent.
- Require minimal editing or review.
- Generate unique, personalized content.
- Inspire creativity and exploration.
Conclusion
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a groundbreaking technology poised to transform how we interact with machines. They can generate text, translate languages, create diverse content, and provide informative answers, fundamentally changing our work, learning, and interactions with the world.
Chapter 2: The Future of AI Conversations
This video discusses the transformative influence of AI on everyday life and the future of human-machine dialogue.
In this TED Talk, experts explore how AI is expected to reshape the global landscape and our daily interactions.
References
- Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners
- On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models
- Basics of Prompting | Prompt Engineering Guide
- A Comprehensive Overview of Prompt Engineering
- www.promptingguide.ai